CBD (CANNABIDIOL)
History of Hemp
Three important definitions to start from.
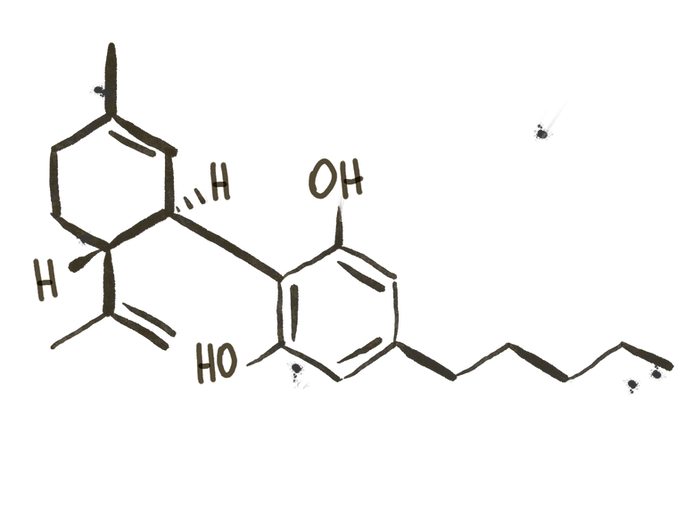
- CBD (or Cannabidiol) is a chemical compound with its own formula (C21H30O2).
- CBD is a phytocannabinoid, which is a cannabinoid produced naturally from a plant. There are 146 phytocannabinoids in cannabis, each with its own characteristics.
- A cannabinoid is “a group of molecules with twenty-one carbon atoms, or as the set of its carboxylic acids and analogues”, words of Professor Mechoulam.
CBD is, together with THC, the phytocannabinoid with the highest concentration within cannabis plants. CBD is particularly concentrated in fiber cannabis varieties (what we commonly call hemp) and does not have the central psychotropic effect of THC.
Each of us has an endocannabinoid system that processes, via receptors, the benefits that each of the cannabinoids and phytocannabinoids brings to the body. The benefits of CBD on our body studied are countless, here are some of the most important:
- It is a natural psychophysical balancer: the endocannabinoid system is one of the main biological centers of our body, its correct function is essential for physical and mental processes to function correctly. CBD acts directly on the endocannabinoid system: stimulates it, protects it, strengthens it.
- It's a painkiller.
- It also reduces the psychotropic effects of THC itself, weakening the hangover symptoms felt.
- It is a stabilizer of intraocular pressure.
- It acts as an antiepileptic, anxiolytic, antibiotic.

ANXIETY
CBD has been shown in numerous animal and human studies to reduce anxiety on its own.
Read more →

SLEEP
CBD has been shown in numerous animal and human studies to reduce anxiety on its own.
Read more →

SPORT
CBD has been shown in numerous animal and human studies to reduce anxiety on its own.
Read more →

PET
CBD has been shown in numerous animal and human studies to reduce anxiety on its own.
Read more →

ENDOCANNABINOID SYSTEM
The endocannabinoid system (EPS) is by definition an endogenous system (which has internal origin) of communication between cells and is of great importance for the regular functioning of the organism. In fact, it takes care of the regulation of pain, inflammation, appetite, hormones, glucose metabolism and the immune response. Cannabinoids act on EPS: endocannabinoids (internally produced cannabinoids) and phytocannabinoids (of predominantly plant origin).
It is the receptors that are responsible for encoding the messages that the cannabinoids carry. Worth mentioning are CB1s which are mainly widespread in the peripheral and central nervous system (they are also partly present in other types of tissues other than nervous such as endocrine glands, the reproductive and urinary systems). CB2 receptors are instead prevalent on immunocompetent cells: in the intestine, liver, spleen, tonsils, lymphocytes,


DIFFERENCE BETWEEN CBD AND THC
Hemp and Cannabis of the same genus and species, Cannabis Sativa. The big difference that has led to distinguishing them is in the concentration of cannabinoids: CBD (a non-psychoactive active ingredient with great relaxing, anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving abilities) is higher in hemp; in Cannabis the THC (the psychotropic active ingredient produced by cannabis flowers) is much higher. This is why the latter has always been referred to in Rastafarian and often derogatory terms, to the point of recognizing it under the name Marijuana which has only brought another element of confusion into the discussion. Only in recent years have cannabis and marijuana been separating their meanings in favor of Cannabis which is often linked to therapeutic use.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is CBD?
Answer
What are terpenes?
Answer
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
Answer







